Types of Software Testing: A Comprehensive Guide
Types of Software Testing: A Comprehensive
Guide
Let’s Explore the Different Types of Software Testing,
Software testing is a critical phase in
the software development lifecycle that helps ensure a software product's
quality, reliability, and functionality.
Several types of software testing serve
different purposes in identifying defects and ensuring that the software meets
its requirements. Here are some of the most common types of software testing
like Functional Testing, Non-Functional Testing, Automation Testing, Agile
Testing, and their sub-types, etc.
Each type of
testing has its features, advantages, and disadvantages. Here we have covered
mostly every type of software testing we usually use in our day-to-day testing
life.
Types of Software Testing:
1. Manual Testing
2. Automation Testing
1. Manual Testing :
What is Manual Testing?
Testing any software
or an application according to requirements without using any automation tool
is known as Manual testing.
We can also say that
it is a procedure of verification and validation.
Classification of Manual Testing:
Manual testing is further classified
into three
different types of testing, which are as follows:
- White Box Testing
- Black Box Testing
- Grey Box Testing
a) White Box Testing:
the code is noticeable for developers throughout testing; this
process is known as White Box Testing.
The
purpose of implementing white box testing is to emphasise the flow of inputs
and outputs over the software and enhance the security of an application
|
. White box testing is also known as open box testing, glass box testing, structural testing, clear box testing, and
transparent box testing. b) Black Box Testing: Black box testing is a process of checking the functionality of an application as per the customer’s requirement. The source code is not visible in this testing that's why it is known as black-box testing. Types of Black Box Testing Black box testing is further categorizes into two parts : Functional Testing Non-function Testing Functional Testing : The test engineer will check all the components systematically against requirement specifications, known as functional testing. Functional testing is also known as Component testing. Types of Functional Testing :Just like another type of testing is divided into several parts, functional testing is also classified into
various categories: Integration testing System Testing 1. Unit Testing Unit testing is the first level of functional testing to test any software. In this, the test engineer will test the module of an application independently or test all the module functionality, called unit testing. The primary objective of executing the unit testing is to confirm the unit components’ performance. A unit is defined as a single testable function of software or an application. 2. Integration Testing Once we successfully implement the unit testing, we will go through Integration testing It is the second level of functional testing, where we test the data flow between dependent modules or interfaces between two features, is called integration testing. Types of Integration
Testing Integration testing is also further divided into the
following parts: Non-Incremental Testing Incremental Integration Testing incrementally adding up the modules and testing the data flow between the modules is known as Incremental integration
testing. Types of Incremental Integration Testing: Incremental integration testing can further classify into two parts, which are as follows:
Top-down Incremental Integration Testing Bottom-up Incremental Integration Testing 1. Top-down Incremental Integration Testing In this approach, we will add the modules step by step or incrementally and test the data flow between them. We must ensure that the modules we add are the child of the earlier ones. 2. Bottom-up Incremental Integration Testing In the bottom-up approach, we will add the modules incrementally and check the data flow between modules. And also, ensure that the module we add is the parent of the earlier ones. Non-Incremental
Integration Testing/ Big Bang Method Whenever the data flow is complex and very difficult to classify a parent and a child, we will use the non-incremental integration approach. The non-incremental method is also known as the Big Bang method. 3. System Testing We can proceed with the system testing whenever we are done with the unit and integration testing. In system testing, the test environment is parallel to the production environment. It is also known as end-to-end testing. In this type of testing, we will undergo each attribute of the software and test if the end feature works according to the business requirement. And analysis of the software product as a complete system. Non-function
Testing : The next part of black-box testing is non-functional testing. It provides detailed information on software product performance and used
technologies. Non-functional testing will help us minimise the risk of production and related software costs. Non-functional testing is a combination of performance, load, stress, usability and compatibility testing. Types of Non-functional
Testing Non-functional testing categorized into different parts of testing, which we are going to discuss further: Performance Testing Usability Testing Compatibility Testing 1. Performance Testing In performance testing, the test engineer will test the working of an application by applying some load. In this type of non-functional testing, the test engineer will only focus on several aspects, such as Response time, Load, scalability, and Stability of the software
or an application. Classification of Performance Testing Performance testing includes the various types of testing, which are as follows: Load Testing Stress Testing Scalability Testing Stability Testing
Load Testing While executing the performance testing, we will apply some load on the particular application to check the application's performance, known as load testing.
Here, the load could be less than or equal to the desired load. Stress Testing It is used to analyse the user-friendliness and robustness of the software beyond the typical functional limits. Stress testing is primarily used for critical software, but it can also be used for all software applications. Scalability Testing To analyse, the application's performance by enhancing or reducing the load in particular balances is known as scalability testing.In scalability testing, we can also check the system, processes, or database's ability to meet an upward need. And in this, the Test Cases are designed and implemented efficiently. Stability Testing Stability testing is a procedure where we evaluate the application's performance by applying the load for a precise time. 2. Usability Testing : Another type of non-functional testing is usability testing. In usability testing, we will analyse the user-friendliness of an application and detect the bugs in the software's end-user interface. 3. Compatibility Testing In compatibility testing, we will check the functionality of an application in specific hardware and software environments. Once the application is functionally stable, we only go
for compatibility testing. Here, software means we can test the application on different operating systems and other browsers, and hardware means we can test the application on different sizes. c) Grey
Box Testing : Another part of manual testing is Grey box testing. It is a collaboration of black-box and white-box testing. Since the grey box testing includes access to internal coding for designing test cases. Grey box testing is performed by a person who knows coding and testing. In other words, we can say that if a single-person team does both white box and black-box testing,
it is considered grey-box testing. 2) Automation Testing : Automation testing involves using specialised software tools or scripts to automate the execution of test cases and compare actual outcomes with expected results. It's beneficial for repetitive tasks, regression testing, and performance
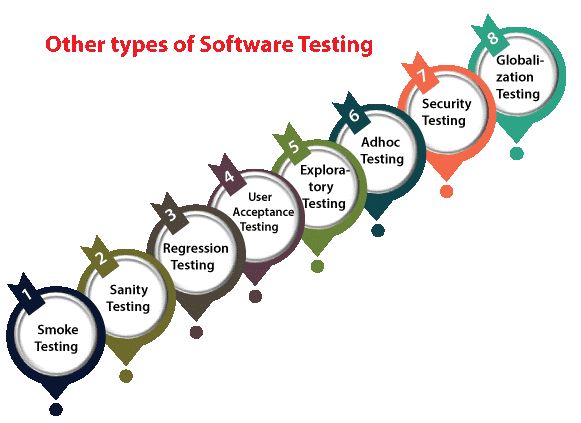
testing. Automation testing is the best way to enhance the efficiency, productivity, and coverage of Software testing. It is used to re-run the test scenarios, executed manually, quickly, and repeatedly. We will go for automation testing when various releases or several regressioncycles go on the application or software. We must understand the programming language in order to write the test script or perform automation testing. Some other types of Software Testing In software testing, we also have other types of testing that are not part of any above-discussed testing, but those tests are required while testing any software or an application. Smoke Testing Exploratory Testing Sanity Testing Adhoc
Testing Regression Testing Security Testing User Acceptance Testing
Globalization
Testing Let's understand those types of testing one by one: Smoke Testing Smoke testing, also known as build verification testing, is a preliminary round of testing to ensure that the most critical functionalities of the software work after a new build or release. It's a quick check to determine if the build is stable enough for further testing. Sanity Testing It is used to ensure that all the bugs have been fixed and that no added issues exist due to these changes. Sanity testing is unscripted, which means we cannot document it. It checks the correctness of the newly added features and components. Regression Testing Regression testing involves re-running tests on the software after changes have been made to ensure that new updates or features have not introduced new defects or broken existing functionality. Automated tests are often used for regression testing to validate the system's behaviour against previously established benchmarks quickly. User Acceptance Testing UAT involves testing the software from the end user’s perspective to ensure that it meets their needs and expectations. This phase often occurs towards the end of the development cycle and involves actual users testing the software in their real-world scenarios. Exploratory Testing Exploratory testing involves testers exploring the software without predefined test cases. Testers use their intuition and creativity to identify defects and issues that scripted tests might not cover. Adhoc Testing Ad-hoc testing is performed without any formal test plan or documentation. Testers randomly test the software based on their understanding of the application, which helps identify unexpected issues. Security Testing Security testing is conducted to identify software vulnerabilities and potential security breaches. This includes testing for data leaks, unauthorised access, and potential exploits. Globalisation Testing Globalisation testing focuses on ensuring that a software application can function seamlessly across different cultures, languages, and regions. Globalisation testing aims to identify and rectify any issues related to internationalisation, which is designing and developing software that can adapt to various cultural and linguistic contexts without requiring code changes. |
Conclusion
:
A combination of
manual and automation testing often provides the best results. While automation
can handle repetitive tasks and provide quick feedback, manual testing brings
human intuition and adaptability to the process, identifying complex issues
that automated scripts might miss. The choice between manual and automation
testing depends on the project's nature, scope, budget, and timeline.











Comments
Post a Comment